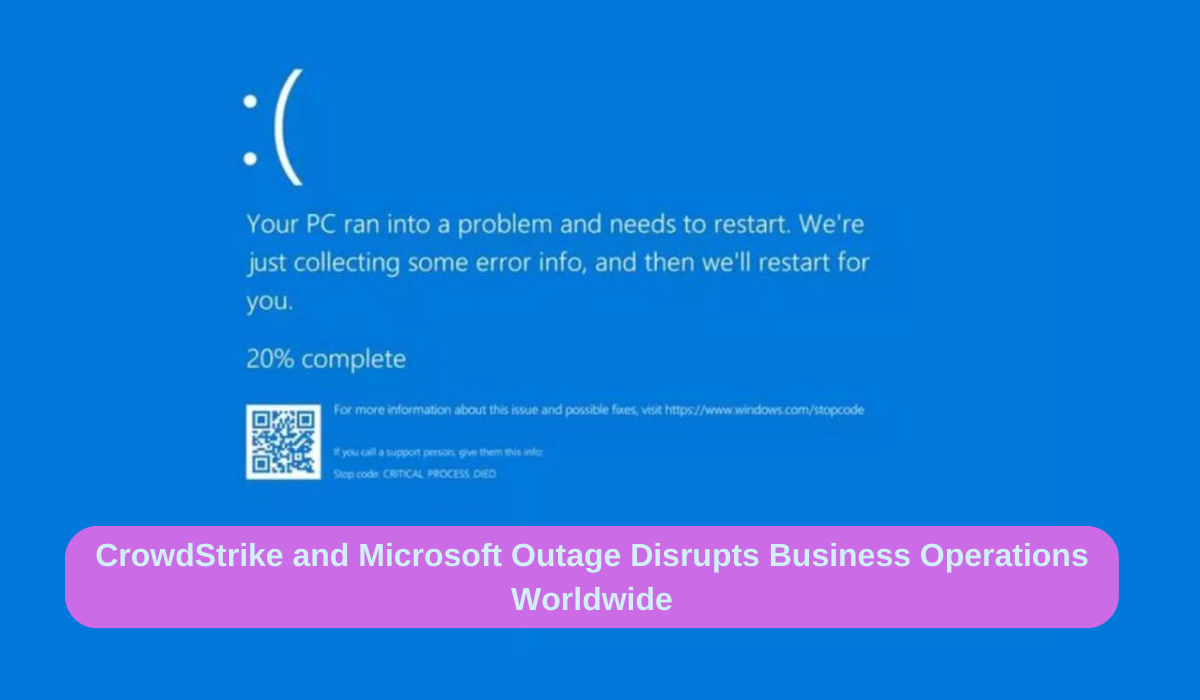
Global Cybersecurity Update: CrowdStrike and Microsoft Outage Disrupts Business Operations Worldwide: businesses and public services worldwide experienced significant disruptions due to a botched update of a widely used cybersecurity program that affected Microsoft Corp. systems. The incident, involving CrowdStrike Holdings Inc. and Microsoft’s Azure cloud service, highlights the vulnerabilities of our increasingly digital infrastructure. This article provides a comprehensive analysis of the event, its impact, and the implications for global business operations.
The Incident: What Happened?
The root cause of the widespread disruptions was a defective update in a cybersecurity program widely used by various organizations. CrowdStrike Holdings Inc. CEO George Kurtz confirmed that the issue had been identified and rectified, assuring stakeholders that it was not a cyberattack but a technical fault. Compounding the situation, Microsoft reported a separate issue with its Azure cloud service, which further exacerbated the outages.
Impact on Businesses and Public Services
The fallout from the update failure was immediate and far-reaching. Key sectors such as airlines, financial services, and customer-facing industries experienced significant operational disruptions:
- Airlines: KLM suspended most flights due to the global computer outage, and Frontier Airlines grounded flights for over two hours, affecting numerous passengers and flight schedules.
- Financial Services: The London Stock Exchange Group (LSE) reported issues that disrupted trading activities, and insurance companies faced operational setbacks.
- Customer Service: McDonald’s Corp. and United Airlines Holdings Inc. disclosed problems in their communication and customer service systems, hampering their ability to serve customers effectively.
Technical Details of the Failure
The issue stemmed from a content update for Windows hosts provided by CrowdStrike. This update caused Windows devices to display blue error screens, preventing access to laptops and corporate computers. While Mac and Linux hosts were unaffected, the widespread reliance on Windows systems meant that the impact was substantial.
The Economic Impact
The economic ramifications of this incident are expected to be significant. Alan Woodward, a professor of cybersecurity at Surrey University, described the event as “unprecedented” and predicted a substantial economic impact. The disruption underscored the interconnectedness of modern business operations and the reliance on digital platforms.
Market Reactions
The stock market reacted swiftly to the news. Shares in CrowdStrike plummeted by 20%, while Microsoft saw a 2.9% decline. This immediate market response highlights investor concerns about the resilience of these tech giants in the face of such disruptions.
Historical Context: Similar Outages
This incident is not an isolated case. There have been several notable IT outages in recent years that serve as a reminder of the fragility of our digital infrastructure:
- Amazon Web Services (AWS) Outage (2017): Errors within AWS disrupted tens of thousands of websites, including ESPN.com.
- Fastly Outage (June 2021): Issues at content delivery network Fastly took down major websites such as the New York Times, Reddit, and Bloomberg News for about a day.
- Amazon’s AWS Outage (Late 2021): Problems with AWS services affected various platforms, including Walt Disney Co. theme parks, Ticketmaster, and Tinder.
These events underscore the critical nature of cloud services and cybersecurity in maintaining operational continuity.
Expert Opinions
Cybersecurity experts have weighed in on the incident, providing insights into its significance and potential long-term consequences:
- Troy Hunt, an Australian security consultant and creator of Have I Been Pwned, described the incident as potentially “the largest IT outage in history,” reflecting the scale and impact of the disruption.
- Alan Woodward highlighted the economic implications, emphasizing the unprecedented nature of the event and its potential to cause substantial economic fallout.
Looking Ahead: Mitigating Future Risks
In light of this incident, it is imperative for organizations to reassess their cybersecurity and IT infrastructure strategies. Here are some key considerations:
Diversification of Cybersecurity Solutions
Relying on a single cybersecurity provider can expose organizations to significant risks in the event of a failure. Diversifying cybersecurity solutions can help mitigate these risks and enhance overall resilience.
Regular Audits and Stress Testing
Conducting regular audits and stress testing of IT systems can identify vulnerabilities and ensure that backup systems are robust enough to handle unexpected failures.
Enhanced Incident Response Plans
Developing and maintaining comprehensive incident response plans can enable organizations to react swiftly and effectively to IT disruptions, minimizing downtime and operational impact.
Collaboration and Information Sharing
Collaboration between companies, cybersecurity firms, and government agencies can facilitate the sharing of information and best practices, enhancing collective defenses against cyber threats and technical failures.
Conclusion
The global disruptions caused by the CrowdStrike and Microsoft outage serve as a stark reminder of the vulnerabilities inherent in our increasingly digital world. By learning from this incident and implementing robust cybersecurity measures, organizations can better prepare for future challenges and ensure the continuity of their operations.
Recommended Diagram
To illustrate the interconnected nature of modern business operations and the impact of IT outages, we recommend a network diagram in Mermaid syntax:
graph TD
A[Businesses & Public Services] -->|Rely on| B[Cybersecurity Programs]
B -->|Provided by| C[Providers like CrowdStrike]
C -->|Linked to| D[Cloud Services]
D -->|Provided by| E[Companies like Microsoft Azure]
E -->|Failures impact| A
D -->|Failures impact| F[Airlines, Financial Services, Customer Service]
F -->|Experience disruptions| AThis diagram visually represents the flow of dependencies and the cascading effects of an IT outage across various sectors.